Lóðurr: Exploring His Elusive Role in Humanity's Origins
Lóðurr is one of the most enigmatic and debated figures in Norse mythology. Mentioned briefly in the Poetic Edda and other sources, he is often linked to the creation of humanity alongside Odin and Hœnir. However, the limited and ambiguous references to Lóðurr have left scholars speculating about his role, identity, and significance in the mythological corpus. While some associate Lóðurr with fire or creative forces, others equate him with other gods such as Loki or Freyr, adding layers of complexity to his characterization.
The Role of Lóðurr in Norse Mythology

Thor’s Hammer Mjölnir Amulet with Othala Rune
The Creation of Humanity
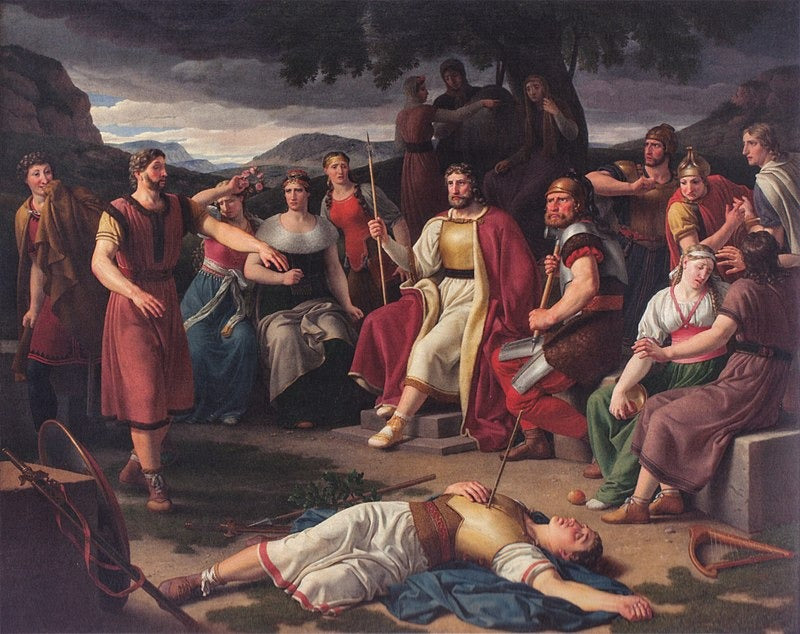
Lóðurr’s most notable mention comes in Völuspá, a poem from the Poetic Edda. In this account, Lóðurr, along with Odin and Hœnir, creates the first humans, Ask and Embla. Odin breathes life into them, Hœnir grants them consciousness, and Lóðurr is credited with bestowing “lá” (possibly meaning blood or warmth) and a “láitir” (likely referring to physical form or beauty). This act situates Lóðurr as an essential figure in the cosmological framework of Norse mythology, associated with the creative and sustaining forces of life.
The Ambiguity of His Role
Despite his involvement in this pivotal myth, Lóðurr’s role in the wider pantheon is unclear. Unlike Odin or Thor, Lóðurr is not a prominent character in other myths, nor does he appear in major sagas or skaldic poetry. His fleeting appearances have led some scholars to suggest that his importance may have diminished over time or that he represents an older layer of Norse belief not fully integrated into the surviving mythological canon.
Theories About Lóðurr’s Identity

Odin, Lóðurr, and Hœnir create the first humans, Askr and Embla (Illustration: Lorenz Frølich)
One of the most debated theories is the identification of Lóðurr with Loki. The two figures share certain creative and fiery attributes, and both are involved in transformative events in mythology. Additionally, a kenning in skaldic poetry describes Loki as “Lóðurr’s friend,” further linking the two. Proponents of this theory argue that Lóðurr may represent a benevolent aspect of Loki’s multifaceted character, aligning with his creative and life-giving role in the creation myth.
Others argue that Lóðurr is synonymous with Freyr, the Vanir god of fertility and prosperity. This theory is supported by Lóðurr’s association with the physical and aesthetic aspects of human life, which align with Freyr’s domain over fertility, beauty, and vitality.
A third perspective holds that Lóðurr is an independent deity whose significance has been largely lost due to the fragmentary nature of Norse sources. As an enigmatic figure, Lóðurr may represent an older or regional god whose worship waned before the consolidation of the Norse pantheon.
Symbolism and Associations

Some interpretations connect Lóðurr to fire, based on his role in imbuing humanity with life and warmth. This symbolism aligns with the life-sustaining and transformative aspects of fire, making Lóðurr a potential personification of the creative energies that animate existence.
Lóðurr’s contribution to humanity’s creation also emphasizes physical beauty and form, suggesting a connection to aesthetics and harmony in nature. This aspect sets him apart from other Norse deities, who are often associated with more abstract or martial attributes.
Lóðurr in Comparative Mythology
The ambiguity surrounding Lóðurr allows for comparisons with figures in other mythological traditions. His role in humanity’s creation parallels Prometheus in Greek mythology, who also brought life and fire to humankind. Additionally, Lóðurr’s elusive nature invites comparisons to deities whose significance has been obscured over time, reflecting the evolving nature of oral traditions and cultural memory.
Legacy and Modern Interpretations

Despite his limited presence in Norse texts, Lóðurr continues to captivate scholars and enthusiasts of mythology. Modern interpretations often highlight his mysterious nature, portraying him as a symbol of the unknown or the forgotten aspects of Norse belief. In contemporary art, literature, and neopagan practice, Lóðurr is occasionally invoked as a creative and life-affirming force, embodying the essential yet often overlooked elements of existence.
Lóðurr’s enigmatic role in Norse mythology underscores the challenges of reconstructing ancient belief systems from fragmented sources. While his contributions to humanity’s creation mark him as a figure of significant importance, his identity and broader role remain subjects of debate. Whether he is an independent deity, an aspect of Loki, or a reflection of Freyr, Lóðurr represents the complexities and richness of Norse mythology, inviting ongoing exploration and interpretation.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- Who is Lóðurr in Norse mythology?
Lóðurr is a figure associated with the creation of humanity, working alongside Odin and Hœnir to give life, form, and beauty to the first humans, Ask and Embla.
- Is Lóðurr the same as Loki?
Some scholars theorize that Lóðurr may be an aspect of Loki, though this interpretation is debated.
- What did Lóðurr contribute to humanity’s creation?
Lóðurr is credited with granting blood or warmth and physical beauty or form to Ask and Embla.
- Why is Lóðurr considered enigmatic?
Lóðurr is only mentioned briefly in Norse texts, leaving his role and identity ambiguous and open to interpretation.
- What is Lóðurr’s connection to fire?
Some interpretations associate Lóðurr with fire, linking him to vitality and the transformative forces of nature.
References
Lindow, John. Norse Mythology: A Guide to Gods, Heroes, Rituals, and Beliefs. Oxford University Press, 2001.
Orchard, Andy. Dictionary of Norse Myth and Legend. Cassell, 1997.
Simek, Rudolf. Dictionary of Northern Mythology. D.S. Brewer, 1993.
Byock, Jesse L. (trans.). The Prose Edda by Snorri Sturluson. Penguin Classics, 2005.
Gylfaginning, The Prose Edda. Translated by Anthony Faulkes, 1987.