Guldhøj Archaeological Discoveries: Unveiling Ancient Danish History
Deep within the rolling landscapes of Denmark, an unassuming hilltop known as Guldhøj has captured the imagination of archaeologists and history enthusiasts alike. This remarkable site, nestled in the heart of Jutland, has yielded a trove of ancient treasures that offer a tantalizing glimpse into the lives and customs of the region's earliest inhabitants. From the awe-inspiring golden artifacts to the remnants of long-forgotten settlements, Guldhøj has become a veritable time capsule, shedding light on a rich and enigmatic past.
Location and Site Overview

Gravhøjen Guldhøj Location, Image by National Museum of Denmark
Geographical Setting
Guldhøj, which translates to "Golden Hill" in English, is located near the town of Jels in southern Jutland, Denmark. The site sits atop a modest hill, overlooking the picturesque countryside that has remained largely untouched by the march of modern development. This geographical setting, combined with the region's favorable soil conditions, has played a crucial role in preserving the archaeological treasures that lay buried beneath the surface for millennia.
Archaeological Significance
The significance of Guldhøj cannot be overstated. Excavations at the site have revealed a wealth of artifacts spanning several centuries, from the Early Bronze Age to the Late Iron Age, making it a critical hub for understanding the evolution of human societies in this region. The discoveries at Guldhøj have not only rewritten chapters of Danish history but have also provided invaluable insights into the intricate web of cultural exchanges and trade routes that crisscrossed ancient Europe.
Major Finds and Excavations

The three oak coffins from Guldhø, image by National Museums Denmark
The Princely Burial
One of the most remarkable finds at Guldhøj was the discovery of a princely burial mound dating back to the Early Bronze Age, around 1500 BCE. This burial site, which had remained undisturbed for over 3,500 years, contained the remains of a high-ranking individual, accompanied by an astonishing array of grave goods. The most captivating of these artifacts was a magnificent golden cup, adorned with intricate spirals and geometric patterns, which has become an iconic symbol of the site's significance.
The Golden Treasures
In addition to the princely burial, Guldhøj has yielded an extraordinary collection of golden treasures, including intricately crafted jewelry, ornaments, and ceremonial objects. These precious artifacts, crafted with remarkable skill and artistry, offer a glimpse into the wealth and sophistication of the region's ancient societies. The golden treasures have also sparked debates among scholars about the role of precious metals in trade, social stratification, and religious practices during that era.
Remnants of Settlements

Wooden Bowls discovered in the coffins
Alongside the burial mounds and golden artifacts, archaeologists have uncovered extensive evidence of ancient settlements at Guldhøj. These remnants, which include post holes, hearths, and pottery shards, provide a tantalizing glimpse into the daily lives of the people who once called this hilltop home. Careful excavation and analysis of these settlements have revealed insights into their agricultural practices, food preparation techniques, and even their architectural styles.
Theories and Interpretations

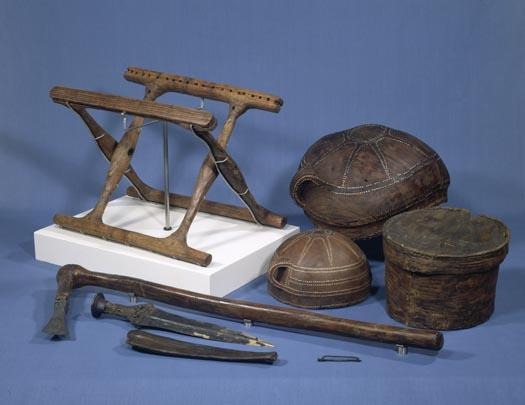
Folding chair of Guldhøj, survived wooden fragments, found in 1891 in Guldhøj near Vamdrup
Social Hierarchy and Power Structures
The discovery of the princely burial and the wealth of golden artifacts at Guldhøj has sparked intense debates among scholars about the social hierarchy and power structures that existed in ancient Danish societies. Some argue that the opulent grave goods and the presence of a high-ranking individual point to the existence of a highly stratified society, with a ruling elite wielding significant power and influence. Others suggest that these artifacts may have been symbols of prestige and status within a more egalitarian social structure.
Religious and Ritual Practices
The numerous ceremonial objects and the presence of burial mounds at Guldhøj have shed light on the complex religious and ritual practices of the region's ancient inhabitants. Scholars have proposed various theories, ranging from sun worship to ancestor veneration, as potential explanations for the intricate rituals and ceremonies that may have taken place at the site. The study of these practices has provided valuable insights into the spiritual beliefs and worldviews that shaped the lives of these ancient peoples.
Trade and Cultural Exchanges
The exquisite craftsmanship and diverse materials found at Guldhøj have led researchers to contemplate the intricate web of trade routes and cultural exchanges that existed during that era. The presence of exotic materials, such as amber and precious metals, suggests that the region was part of a vast network of trade and cultural exchange, stretching across ancient Europe and beyond. This has opened up new avenues of research into the economic and cultural connections that bound these distant communities together.
Preservation and Museum Exhibits
On-Site Conservation Efforts
Recognizing the immense historical and cultural significance of Guldhøj, concerted efforts have been made to preserve and protect the site for future generations. On-site conservation measures have been implemented to safeguard the remaining archaeological features and prevent further deterioration. These efforts include careful excavation techniques, environmental monitoring, and the construction of protective shelters over sensitive areas.
Museum Displays and Accessibility
To share the wonders of Guldhøj with the world, many of the site's most remarkable finds have been meticulously curated and displayed in various museums across Denmark. The National Museum in Copenhagen houses an extensive collection of artifacts from the site, including the iconic golden cup and intricate jewelry pieces. Additionally, local museums in the Jutland region have created immersive exhibits that allow visitors to experience the rich history and cultural heritage of Guldhøj firsthand.
Continuing Research and Future Prospects
Despite the wealth of knowledge already gleaned from Guldhøj, the site remains an active area of archaeological exploration and research. New excavation techniques and advanced analysis methods continue to shed light on previously unexplored aspects of the site's history. Ongoing collaborations between archaeologists, historians, and specialists from various disciplines promise to unravel even more mysteries and deepen our understanding of the intricate tapestry of ancient Danish societies.
Conclusion
Guldhøj stands as a testament to the enduring allure of archaeological discoveries and their ability to transport us through time. This unassuming hilltop has yielded a treasure trove of artifacts that have not only captivated the imagination but have also challenged our perceptions of the past. From the awe-inspiring golden treasures to the remnants of long-forgotten settlements, Guldhøj has become a window into the rich tapestry of ancient Danish history, offering a tantalizing glimpse into the lives, beliefs, and customs of those who came before us. As we continue to unlock the secrets buried beneath the earth, sites like Guldhøj serve as powerful reminders of our shared heritage and the enduring human quest for knowledge and understanding.
FAQs
- What is the significance of the golden artifacts found at Guldhøj?
- The golden artifacts, such as the iconic cup and intricate jewelry pieces, are not only remarkable examples of ancient craftsmanship but also provide insights into the wealth, status, and cultural practices of the region's ancient societies. These precious objects have sparked debates about social stratification, trade networks, and religious rituals.
- How old are the archaeological remains at Guldhøj?
- The archaeological remains at Guldhøj span a vast period, ranging from the Early Bronze Age (around 1500 BCE) to the Late Iron Age (around 800 CE). This long timeframe allows researchers to study the evolution of human societies in the region over several millennia.
- What kind of settlements were discovered at Guldhøj?
- Excavations at Guldhøj have uncovered remnants of ancient settlements, including post holes, hearths, and pottery shards. These findings provide valuable insights into the daily lives, agricultural practices, and architectural styles of the people who once inhabited this hilltop.
- Why is Guldhøj considered an important site for understanding cultural exchanges in ancient Europe?
- The presence of exotic materials, such as amber and precious metals, at Guldhøj suggests that the region was part of a vast network of trade and cultural exchange stretching across ancient Europe and beyond. This has opened up new avenues of research into the economic and cultural connections that bound distant communities together.
- How are the archaeological finds from Guldhøj being preserved and exhibited?
- Significant efforts have been made to preserve and protect the Guldhøj site for future generations. On-site conservation measures include careful excavation techniques, environmental monitoring, and the construction of protective shelters. Additionally, many of the site's remarkable finds have been meticulously curated and displayed in various museums across Denmark, allowing visitors to experience the rich history and cultural heritage of Guldhøj firsthand.
Folding chair of Guldhøj, survived wooden fragments, found in 1891 in Guldhøj near Vamdrup
Citations:
National Museum of Denmark. (n.d.). A folding chair from the Bronze Age. [online] Available at: https://en.natmus.dk/historical-knowledge/denmark/prehistoric-period-until-1050-ad/the-bronze-age/a-folding-chair-from-the-bronze-age/.
National Museum of Denmark. (n.d.). A vessel with tin tacks. [online] Available at: https://en.natmus.dk/historical-knowledge/denmark/prehistoric-period-until-1050-ad/the-bronze-age/a-folding-chair-from-the-bronze-age/a-vessel-with-tin-tacks/ [Accessed 19 Mar. 2024].
National Museum of Denmark. (n.d.). An elegant seat of otter skin. [online] Available at: https://en.natmus.dk/historical-knowledge/historical-themes/the-fur-trail/fur-in-prehistory/an-elegant-seat-of-otter-skin/ [Accessed 19 Mar. 2024].
National Museum of Denmark. (n.d.). Grave robberies. [online] Available at: https://en.natmus.dk/historical-knowledge/denmark/prehistoric-period-until-1050-ad/the-bronze-age/the-people-in-the-bronze-age-barrows/grave-robberies/ [Accessed 19 Mar. 2024].
National Museum of Denmark. (n.d.). The graves from Guldhøj. [online] Available at: https://en.natmus.dk/historical-knowledge/denmark/prehistoric-period-until-1050-ad/the-bronze-age/a-folding-chair-from-the-bronze-age/the-graves-from-guldhoej/ [Accessed 19 Mar. 2024].
'Wooden Bowls' image by Lennart Larsen is licensed under CC-BY-SA
'Folding chair from Guldhøj' by Roberto Fortuna and Kira Ursem is licensed under CC-BY-SA