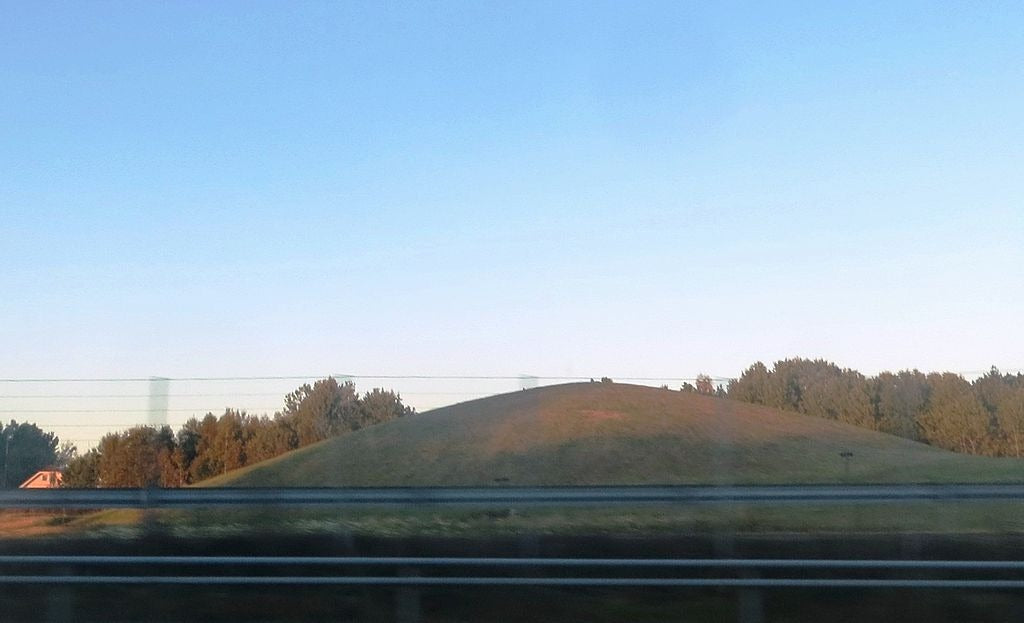
Ancient Viking Ship Found Near Gjellestad, Norway
The discovery of the Gjellestad Ship has added a significant chapter to the annals of Viking history. Unearthed by the Museum of Cultural History and Østfold County Authority (now Viken County Authority) at Gjellestad outside Halden, this Viking ship burial promises to shed new light on the Viking Age, particularly in relation to power dynamics and societal structures. While much has been revealed, the ship continues to hold many secrets waiting to be uncovered.
The Discovery and Initial Findings
Last fall, a pivotal moment in Viking archaeology occurred when archaeologists successfully located the keel of the Gjellestad Ship. This discovery has provided substantial insights into the ship's origins and the period it belongs to. Although exact dating remains elusive due to missing parts of the wood, analyses indicate that the timber used in the ship was felled after 732 AD. Consequently, it is believed that the ship burial dates to between the late 700s and the early 900s, placing it firmly within the first half of the Viking Age.
Christian Løchsen Rødsrud, the project manager during the excavation, notes that this timeframe aligns the Gjellestad Ship with other major Viking ship finds in Norway, such as the Oseberg and Gokstad ships. This correlation not only places the Gjellestad Ship within a known historical context but also enhances our understanding of Viking ship burials.
Social and Political Implications
While no human remains have been discovered yet, it is widely believed that the Gjellestad Ship served as the burial site for a person of considerable significance, likely from the upper echelons of society. This hypothesis is supported by comparisons to other notable Viking burials, such as the Oseberg ship burial, which contained two women of high status, along with the Gokstad and Ladby burials. Therefore, it is plausible that the Gjellestad burial could also involve multiple individuals.

Gjellestad Ship Excavation / Photo: Museum of Cultural History
The period during which the Gjellestad Ship was buried was marked by a complex web of power relations. The Oslo Fjord region, where the Gjellestad Ship was found, was a hotspot of chieftain-led communities vying for dominance. The presence of large burial mounds and status symbol ships on both sides of the fjord underscores the importance of these burial sites in asserting power and influence.
Rødsrud suggests that the discovery of the Gjellestad Ship might challenge previously held notions about the centers of power during the Viking Age. Historically, the western side of the Oslo Fjord has been considered the primary locus of power due to the prominent ship finds there. However, the Gjellestad Ship, along with the previously discovered Tune Ship in Østfold, indicates a significant power presence on the eastern side as well.
Historical Continuity and Archaeological Significance
The Gjellestad area is notable for its long history of human activity, spanning from approximately 1500 BC through various historical periods. This site boasts a rich tapestry of discoveries, including settlements from the pre-Roman Iron Age around 500 BC and over 15 known graves, with the likelihood of more yet to be discovered.
One of the most prominent features in the area is Jellhaugen, Norway's second-largest burial mound, constructed around 500 AD. By the time the Gjellestad Ship was buried, this area had evolved into a significant burial ground, reflecting a continuity of use that stretches back centuries. This longstanding association with burial practices highlights the sacred and symbolic importance of the site.
The Keel and Further Excavations
The keel of the Gjellestad Ship has been a focal point of interest for archaeologists. Its smaller size compared to other known Viking ships has raised questions about the ship's construction and purpose. While further excavation might reveal more about the ship's design, there is hope that preserved elements such as the mast could confirm whether it was a sailing vessel.

Remnants of the Gjellestad Ship's keel / Photo: Museum of Cultural History
Comparative studies with other Viking ships, including those found in western Norway, suggest that the Gjellestad Ship may have been constructed on the west or southwest coast. Further research and potentially more wood samples from the site could provide a more precise origin for the ship's timber.
Potential Grave Goods and Rituals
Despite the challenging conditions for preservation, there is optimism about uncovering more artifacts within the Gjellestad Ship. The area excavated last fall had the poorest preservation conditions, yet hopes remain high for discovering floor panels, a burial chamber, and items that accompanied the deceased. These could include weapons for a male burial or jewelry for a female, alongside household items and possibly even traces of ritualistic animal sacrifices.
The Broader Gjellestad Complex
The surroundings of the Gjellestad Ship are equally intriguing. Indications suggest the presence of a nearby market area, similar to what has been found near the Gokstad Ship. This commercial site, if confirmed, could enhance our understanding of the economic activities and daily life during the Viking Age.
The urgency to excavate the remaining parts of the Gjellestad Ship cannot be overstated. The site has undergone significant changes since the late 1800s, including the removal of the burial mound and soil drainage, which have accelerated the degradation process. Without timely intervention, invaluable historical information could be lost.
Conclusion
The Gjellestad Ship stands as a testament to the rich and complex history of the Viking Age. Its discovery and the subsequent findings have already provided valuable insights into the period's social structures, power dynamics, and burial practices. As excavations continue, we anticipate that the Gjellestad Ship will further illuminate our understanding of this fascinating era, offering a deeper connection to the lives and traditions of the Vikings.
FAQs
- What is the Gjellestad Viking Ship?
The Gjellestad Viking Ship is a 9th-century burial ship discovered in Gjellestad, Norway. It provides a unique glimpse into Viking shipbuilding, burial practices, and cultural beliefs.
- Why is the Gjellestad Viking Ship significant?
The ship's discovery has advanced our knowledge of Viking history, offering insights into their craftsmanship, maritime technology, and social hierarchy.
- What artifacts were found with the Gjellestad Viking Ship?
Excavations revealed artifacts such as weapons, tools, pottery, and textiles, providing a comprehensive view of Viking daily life and burial customs.
- What technologies were used in the study of the Gjellestad Viking Ship?
Modern techniques like DNA analysis, carbon dating, and 3D scanning were employed to analyze the ship's structure, materials, and historical context.
- What are the future plans for the Gjellestad Viking Ship?
Conservation efforts are ongoing to preserve the ship, with plans for a museum exhibit to educate the public about its historical significance.
References
National Geographic. (2019). Viking Ship Discovered Buried in Norway. National Geographic.
Norwegian Institute for Cultural Heritage Research (NIKU). (2020). The Gjellestad Viking Ship. NIKU.
BBC News. (2019). Norway Viking Ship Grave Found in 'Good Condition'. BBC News.
University of Oslo. (2021). The Gjellestad Ship - A Viking Age Ship Find. University of Oslo.
The Viking Ship Museum. (2022). The Gjellestad Ship. The Viking Ship Museum.